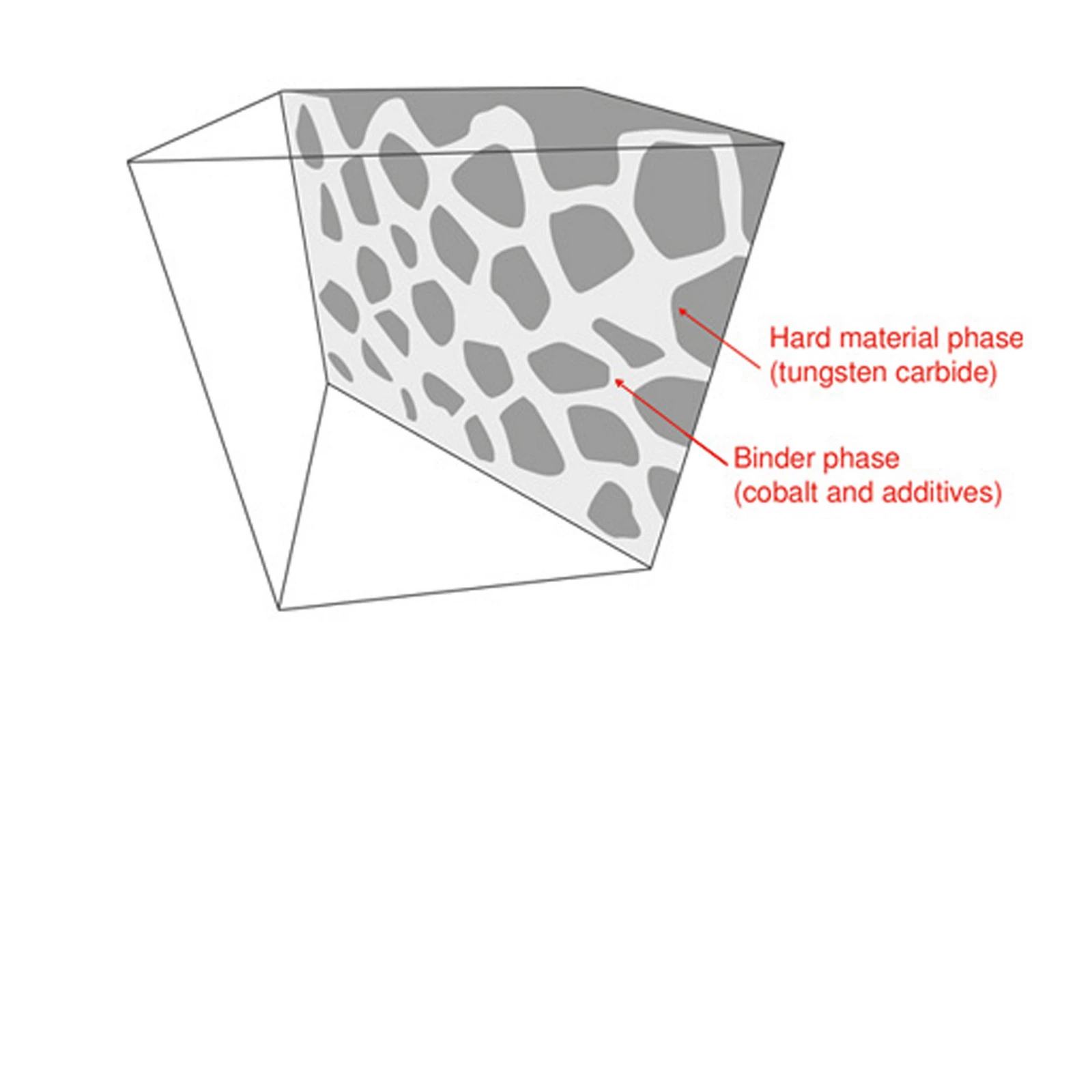
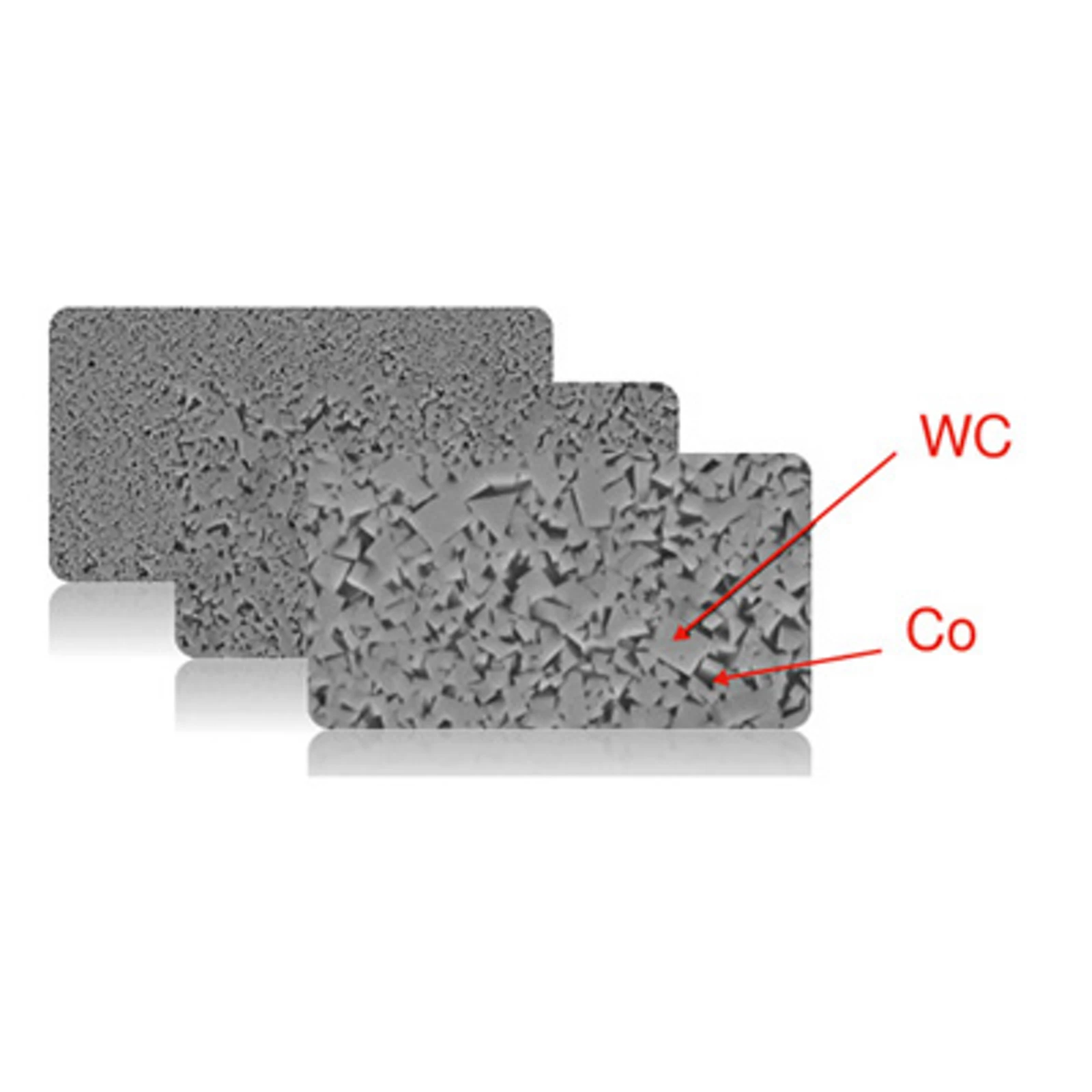
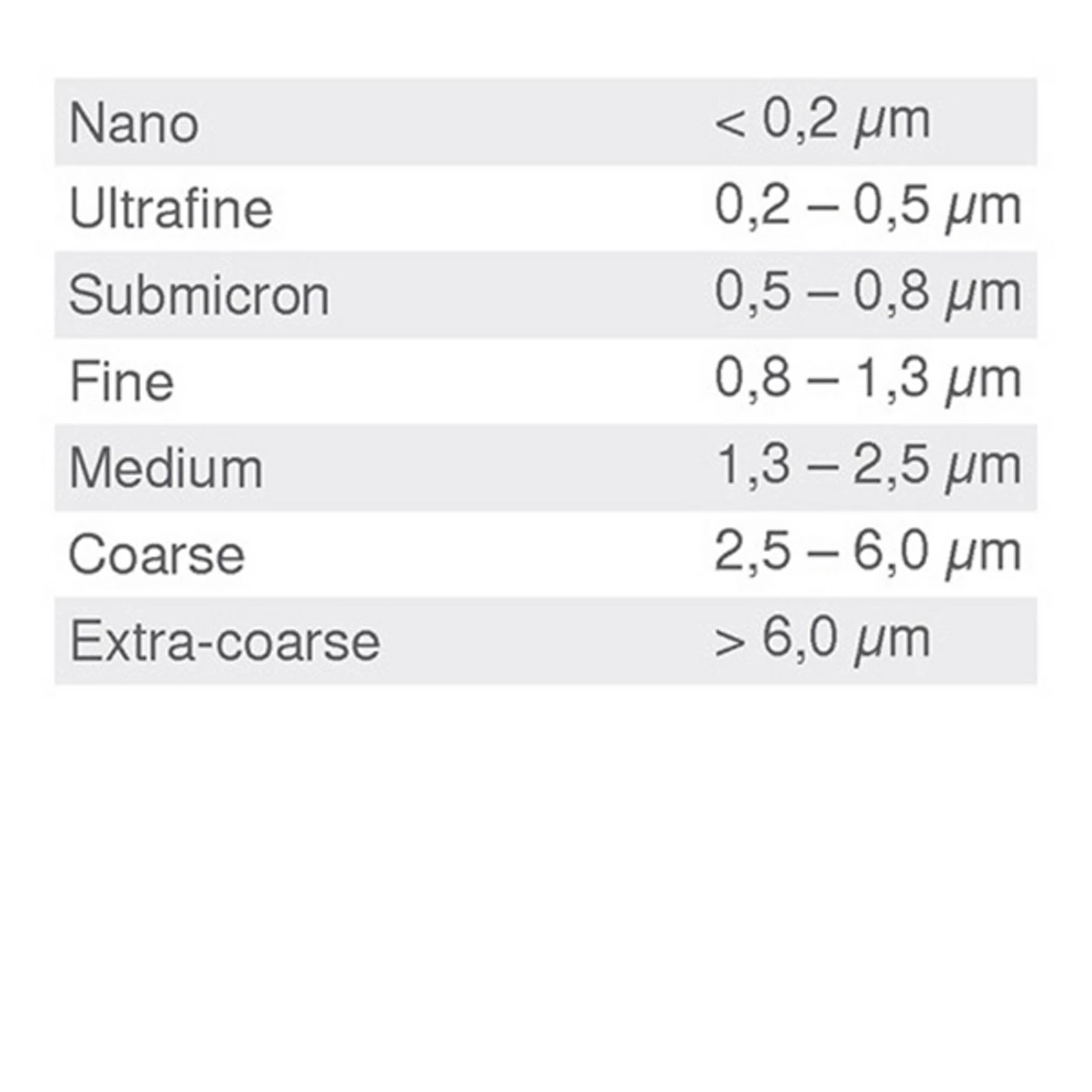
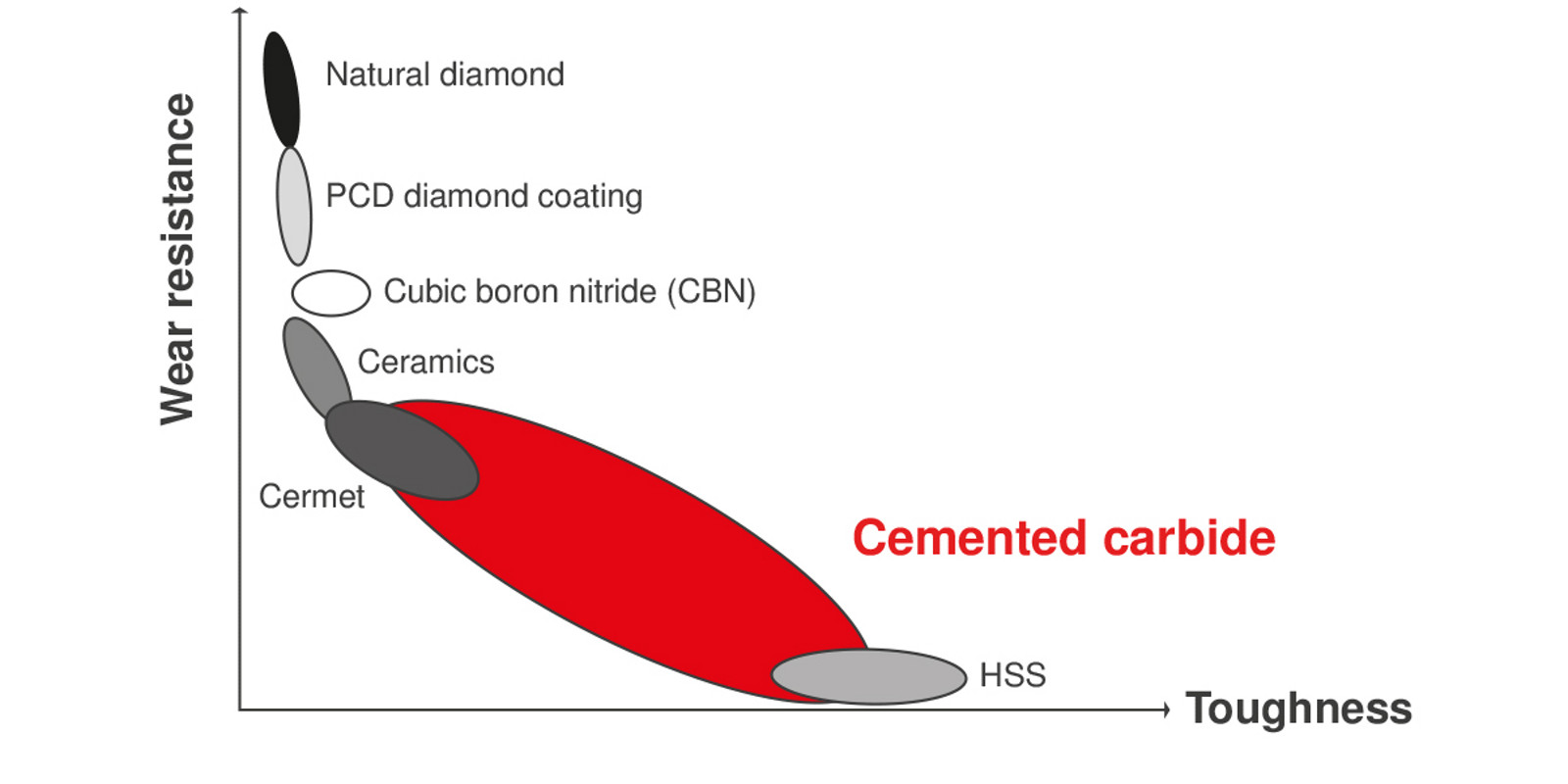
Carbide is a powder-metallurgical two-phase material consisting of a hard material phase and a metal binder phase. The hard material provides the necessary hardness (= wear resistance) and the binder metal guarantees appropriate toughness.
In the case of cemented carbides for cutting tools and wear protection, tungsten carbide (WC) is generally used as a hard carbide phase and cobalt (Co) as metal binder (binder phase). The reason for this is that applying this combination the best physical and mechanical properties can be obtained.